

When the gate voltage is increased more than the source voltage, the charge carriers (holes) shifts away leaving behind the electrons and thus a wider channel is established. In this mode, there is no conduction at zero voltage which implies it is closed or “OFF” by default as there is no existing channel. On the basis of Operational Mode, MOSFETs can be classified into two types.įig.2 – Types of MOSFET Enhancement Type MOSFET The gate terminal is insulated whose voltage regulates the conductivity of the device.
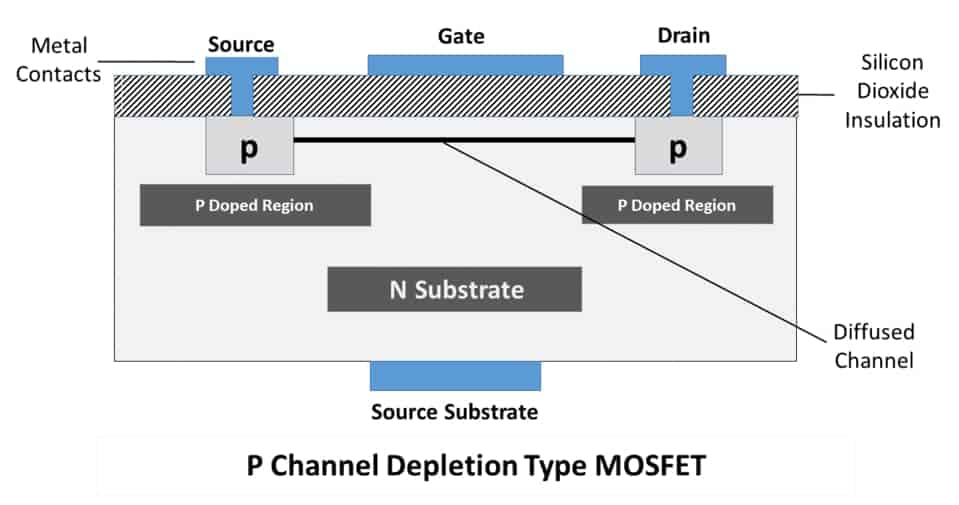
It works by altering the width of the channel through which the movement of charge carriers (electrons for N-channel and holes for P-channel) occurs from source to drain. It is fabricated by the oxidation of silicon substrates. Working Principle of MOSFETįig.1 – Structural and Physical View of MOSFET The Silicon di-oxide (SiO2) layer acts as an insulator and provides electrical isolation between the gate and an active channel between the source and the drain which provides high input impedance which is almost infinite thus capturing all the input signal. In recent years, its discovery has led to the dominant usage of these devices in digital integrated circuits due to its structure. Apart from these terminals there is a substrate generally called the body which is always connected to the source terminal for practical applications. The device has three terminals consisting of a source, gate and drain. It is merely a unipolar transistor and used as an electronic switch and to amplify electronic signals. Metal Oxide Silicon Field Effect Transistor is abbreviated as MOSFET. Bipolar Junction Transistor – Definition, Construction, Types & Applications What is MOSFET


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
